ACT-R Spring School
After the Spring School, I will also present my recent work on the First European ACT-R Workshop. In this talk, I will discuss an experimental paradigm used in multiple-choice decision-making research, and present a model very much in line with RACE/A that may explain some complex interactions that we have observed in the paradigm.
New postdoc position at University of Amsterdam
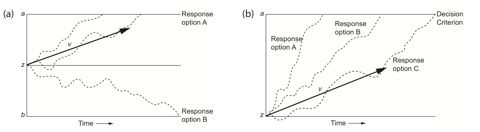
Models of decision-making
Recent publications
December 2009:
Van Maanen, L., Van Rijn, H., & Borst, J.P. (2009). Stroop and Picture-Word Interference are Two Sides of the Same Coin. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(6), 987-999. pdf
A paper that discusses a peculiar difference between the Stroop effect and picture-word interference with the general opinion that these effects are similar.
January 2010:
Van Maanen, L., Van Rijn, H., Van Grootel, M., Kemna, S., Klomp, M., & Scholtens, E. (2010). Personal Publication Assistant: Abstract recommendations by a cognitive model. Cognitive Systems Research, 11(1), 120-129 (Special Issue on Brain Informatics). url pdf
A paper that introduces a system that provides relevant scientific literature based on the user’s own publication record. The system is based on a formal theory of human memory, arguing that recommender systems that model a user’s memory capabilities are useful in predicting relevance. This paper is the direct result of a course I taught in 2007 in which the students and I explored various options of using models of memory in recommender systems!
Expected January 2010:
Van Maanen, L., & Van Rijn, H. (2010). The Locus of the Gratton Effect in Picture-Word Interference. TopiCS in Cognitive Science 2(1), 168-180. pdf
This paper shows that sequential effects in picture-word interference may influence the locus of the interference effect. In addition, it discusses a model that accounts for the observed effects.
Winner Best Student Paper at ICCM

The paper describes how cognitive control may determine not only the effect size of picture-word interference, but also the stage in a task in which the interference occurs. Using a RACE/A model we show that the apparent shift of the interference effect from a late to an early effect locus may be the result of a decrease of the cognitive control on reading the word (of the picture-word stimulus).
Cognitive Modeling on LinkedIn
Click the image to join!

(Also check out the Facebook group :-)).
