


Next: Software structure of
Up: Architectures and
Interaction
Previous: A framework for
In the former ESPRIT II project 2474, ``MMI2: A Multi Mode Interface
for Man Machine Interaction with knowledge based systems'', the
architecture shown in figure 4.2 has been developed for a
multimodal UI [22]. The interesting thing to notice about this
approach is that it deals not only with informations but also with the
meaning of it.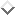 In figure 4.2 , this is represented by the arrows
marked with CMR, the Common Meaning Representation. With
respect to multimodality, the MMI2 system supports a graphic and a gesture
mode as well as several different language modes (command, Spanish, French,
English). One of the main benefits is the integration of all these modes
which are managed by the system itself.
In figure 4.2 , this is represented by the arrows
marked with CMR, the Common Meaning Representation. With
respect to multimodality, the MMI2 system supports a graphic and a gesture
mode as well as several different language modes (command, Spanish, French,
English). One of the main benefits is the integration of all these modes
which are managed by the system itself.
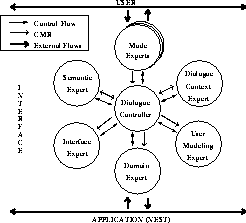
Figure 4.2
: General architecture of the MMI2 system [CMR: Common Meaning
Representation] (Taken from [22])
One of the basic assumptions that lead to this architecture is that
``mode integration should mainly be achieved by an integrated management
of a single, generalized, discourse context.''
The second basic architectural principle is that
``there is a meaning representation formalism, common to all modes, which
is used as a vehicle for internal communication of the semantic content
of interactions inside the interface itself and also used as a support
for semantic and pragmatic reasoning.''
Although this architecture has been especially designed with the
application of knowledge based systems in mind, it can easily be adapted
for the purposes of . The tasks of the `experts' shown in
figure 4.2 will not be further described here with two
exceptions: The user modeling expert which maintains and exploits
the user mode' and the semantic expert which has all the knowledge
about the general properties of meaning concepts. These two are of special
interest to because both a user discourse model and a semantical
representation might be necessary in order to strive for meaning or to find
the user's intention.



Next: Software structure of
Up: Architectures and
Interaction
Previous: A framework for
 Esprit Project 8579/MIAMI (Schomaker et al., '95)
Esprit Project 8579/MIAMI (Schomaker et al., '95)
Thu May 18 16:00:17 MET DST 1995
![]() In figure 4.2
In figure 4.2 