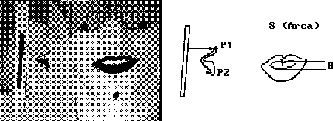
Figure C.7 : An example of an image frame and the visual parameters
A probabilistic approach, i.e. the HMM is used as the main classifier.
The system has first been developed using an off-line analysis of the
lips [171]. In order to extract the necessary visual information
from the talker's face, the speaker's lips are made up in blue. A
chroma-key turns it on-line into a saturated black color. Therefore the
vermilion area of the lips is easily detected by thresholding the luminance
of the video signal. Finally, these images are used as the input of an
image processing software which measures the parameters used for the visual
recognition system. Figure C.7
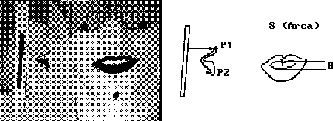
Figure C.7
: An example of an image frame and the visual parameters
The parameters are extracted from each video field (50 fields in a one
second sequence). They are stored in a file used as the main ``optical
data'' input of our visual speech recognizer. The audio input is a vector
composed of a total of 26 elements such as Mel-frequency cepstral
coefficients, energy, delta coefficients. In order to have a complete
synchronization between audio and visual information cues, a 20 msec audio
analysis window has been used. Therefore, visual and audio vectors are in
synchrony during all the process. As a first step towards building an
audio-visual speech recognizer, we followed the architecture of the Direct
Identification Model (see MIAMI report 94-2 by Robert-Ribes). The video
parameters are appended to each audio vector. Several tests have been run
in order to choose the best combination of visual parameters. Finally, only
four parameters have been selected as the input of the speech recognition
system. They are presented in figure C.7