Software
This page is meant as a starting -and reference point for implementations and demo-software of the protocol described in the article New Protocols for Proving Knowledge of Arbitrary Secrets While Not Giving Them Away, by Wouter Teepe (past graduate student of the Multi-Agent Systems Group), which was presented at the Knowledge and Games Workshop in 2004. This paper introduces and describes new protocols for proving knowledge of secrets without giving them away: if the verifier does not know the secret, he does not learn it.


















Proving Possession Of Arbitrary Secrets
This site is about knowledge-based algorithms for multi-agent communication. On this site a simulation can be found wich gives insight in the one-on-group communication algorithm as presented by Egon van Baars and Rineke Verbrugge in their paper Knowledge-based Algorithm for Multi-Agent Communication. To view the simulation klick on the menu item "Simulation". The buttons and the interface of the simulation are explained in the manual section of the site.
One-On-Many Communication
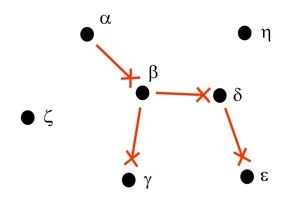
Computing Credulous Acceptance and Rejection in Argumentation
CompArg is a tool for the computation of credulous acceptance and rejection for Dung-style argumentation frameworks. The program computes minimal admissible sets containing and attacking the arguments in a theory. It also produces the grounded extension and all preferred extensions (which include the stable extensions).
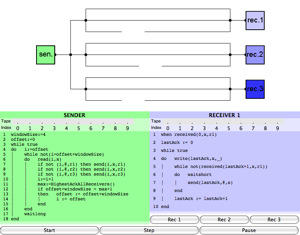
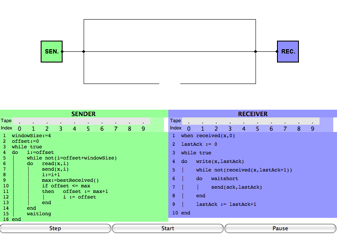
This page describes the knowledge-based algorithms modelling the Transmission Control Protocol, and goes with an article that has been presented at the LOFT4 conference at the ICER institute in Torino, Italy, on 30 June 2000 and at the Tenth Annual CSLI LLC Workshop at Stanford University on 26 May 2001. It has also been published in the Bulletin of Economic Research: Stulp&Verbrugge2001.pdf.
Visualization of the TCP Protocol
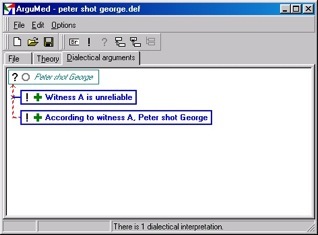
Automated Argument Assistance
Argument assistants are computer programs that support argumentative tasks. The ArguMed system is a research prototype of an argument assistant. It has been designed to construct and visualize warranted defeasible arguments. Statements are evaluated (as justified, defeated or open) because ArguMed implements the defeasible logic DefLog.