Note: the content of this page might change slightly; be sure to refresh right before you start

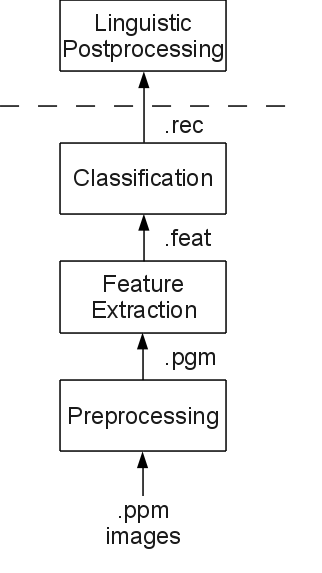
The goal of this assignment is to preprocess the available images. That means
transforming the colour images (in .ppm format) to gray-scale images (in
.pgm format) and removing noise.
This is step 1 of the pipeline shown in the image to the right.
You will produce a script or program called prepro. The arguments that will
be passed to this program are original.ppm preprocessed.pgm. The first
argument is an existing file, which must be read. The second argument is the
file which should be written.
Hand in your code in a .tar.gz file, marked with your name and assignment
number. If there are compilation steps, create a Makefile, which compiles
your program with a single make command.
Your code should have a basis in the literature. Be sure to look through the papers provided on preprocessing. Put comments in your code detailing the steps you took and on which articles you base your method.
toolbox/These files are located in /home/student/vakken/hwr/toolbox. You can copy
these to your own working directory.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
pamImage.cpp |
Read and write .pbm / .pgm / .ppm files (you don’t need to look inside this file) |
pamImage.h |
Header for pamImage.cpp; look here to see what you can do with a PamImage object. |
pamImage.i |
Interface between C++ and Python for pamImage. Swig uses this file to create a Python wrapper around the C++ code |
cocos_arnold/ |
C++ routines for fast connected components labeling by Arnold Meijster (no need to look inside). |
cocoslib.cpp |
Procedures to compute connected components in document images (uses cocos_arnold/). |
cocoslib.h |
Header for cocoslib.cpp. |
cocoslib.i |
Interface between C++ and Python for cocoslib |
example_cocos.py |
Provides a quickstart for using connected components. |
Last modified: April 27, 2011, by Jean-Paul van Oosten
Part of the HWR course